Down Tor Stone Circle Down Tor Stone Circle is a stone circle near Down Tor, Dartmoor. Also called Hingston Hill Cairn. Foggintor Quarry is not far to the northwest, where the stones could have been quarried, along with Down Tor, which is currently a national park. Crazywell Cross is to the north and Drizzlecombe to the south. Coordinates 50.506060,-3.994103 Description Down Tor Stone Circle consists of a long stone row with a circle of stones at the end towards the southwest. This can be considered similar to Drizzlecombe in shape and construction, and is 2 kilometers away. Measurements This tor and circle are angled at 22° towards the southwest, with the row at a length of 755 feet or 230 metres. Analysis It is possible that Down Tor Stone Circle is similar to Drizzlecombe, which was shown to be possibly connected with the golden ratio and π or 9πφ together. The circle is 40 meters wide. If using the 22° on the circle towards the northwest, then all stones pair...
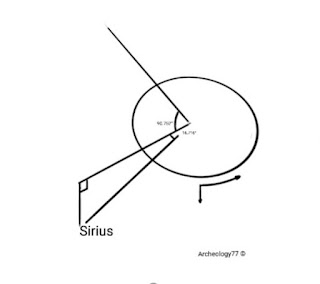
Measuring star separation distances.
The use of a gnomon in solar measurements is usually limited to between 28°-78° latitudes. This is because a gnomon relies on casting a shadow on the ground. Nearer the equator little or no shadow is cast and further north the light intensity is reduced such that it is difficult to measure. Other devices like a quadrant could also measure inclination.
Angles used in measuring stars, max tilt, obliquity, and equatorial tilt.
20°
1.43° (1.2°)
7.155°
The 0.0392°/day variation along 7.155 equatorial tilt using a distance of 1km to define the horizon angle of 1.0145° with sides of 0.962km/0.042km with a perimeter of 2km. This is a gnomon measurement for east/west and maintains the horizon.
1.0145°/day =365÷1.0145=360
68.67 days or 2.289 months
(=5.32 readings per year)
Here, the errors are defined, and then readings can be taken.
Horizontal
1.0145°/day =365.2425÷360=1.0145°
Vertical
0.0392°/day =14.31÷365.2425=360°
Tilt (rotational)
20÷(25772÷2)=0.00155°
=0.00155×1000=1.55°/1000 years
Obliquity (decreasing)
2.86÷20500=0.0001395°/year
2.40÷20500=0.000117°/year
Obliquity should be considered as subtracting from an increasing tilting in the last 8600 years, and as tilt is decreasing from the 1980s, it should be considered as adding.
Obliquity
Using two numbers, 1.43° an ancient Egyptian derived number and a mean modern day number of 1.2° for obliquity.
Currently considered as a fluctuation from 22.1° to 24.5° about the current tilt of 23.5°, but the exact number is 23.253° as a point. This gives a difference of 1.247° from 24.5° as peak and decreasing and shall continue to do so.
Mid point for 1.43° =23.253° (24.68° peak)
10250÷1.43
7167.832×0.1855=1329
10250-1329=8921-2019=6902 bc
(Difference from 2019, 23.437−23.253=0.1855)
Mid point for 1.2° =23.253° (24.5° peak)
10250÷1.2
8542×0.1855=1584
10250-1584=8665-2019=6646 bc
Obliquity tilt was at its peak 6902 bc or 6646 bc, its precession is for 41000 years, so peak to mid point in 20500 years is 10250 years.
According to recent calculations, the mid point is 23.253° about a 2.4° fluctuation, which hasn't been reached yet.
23.253−23.439=0.1855
0.1855÷0.0001395=1329 years
Peak=(10250−1329)−2019=6902 bc
0.1855÷0.000117=1584 years
Peak=(10250−1584)−2019=6642 bc
A difference of 256 years
So, for the last 20500 years, obliquity was trying to cancel tilt by 1.43°.
15.89°-1.43°.
But from 1980's tilt has been decreasing so for the following 10250 the tilt is
15.89°+1.43°
But obliquity is for 20500 years, so this equates to 9981 years.
Recent calculations suggest the fluctuation is 1.2° about 23.253°
This is 23.4385-23.253=0.1855° away from mid point.
=1584 years from mid point (2011 numbers)
(10250−1584)−2019=6646 bc
So from 2011=6654 bc
As a percentage difference
(12886÷100×67)−1984=6650 bc
After the errors.
Horizontal
1.0145°/day =365.25÷360=1.0145°
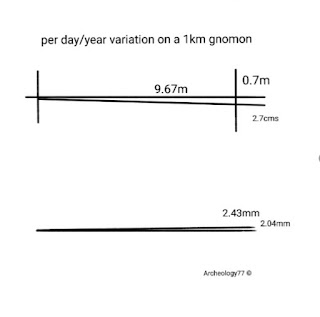
1° of variation =51.6-42=9.67m
Vertical
0.0392°/day =14.31÷365.25=360°
1° of variation =25.5 days=18m
=0.7m /day
Tilt (rotational)
20÷(25772÷2)=0.00155°
=0.00155×1000=1.55°/1000 years
1° of variation =645 years
=0.00155°/year=2.7cms/year
Obliquity (decreasing)
2.86÷20500=0.0001395°/year
1° of variation =7167 years
=2.43mm
2.40÷20500=0.000117°/year
1° of variation =8542 years
=2.04mm
These numbers can be adjusted for a 360-day year, and the difference is small, but the use of 1.0145 and not 1.0 suggests that they used a 365.25 day year. Measure for the obliquity probably got averaged out over a 10 year duration, and tilt might have been the same.
Measuring stars
For example, the star Sirius at:
Right ascension
06h 45m 08.91728s
=90.752°
Declination
−16° 42′ 58.0171″
=16.716°
Measures could be used to mark their location for any given year, and as it rotates, the displacement can be measured. The displacement would contain both the error and objects variation, where the error could be subtracted.
Solar Elevation Angle
Temperature Trend Changes
Orbital Climate Change
Archeology77 ©
The use of a gnomon in solar measurements is usually limited to between 28°-78° latitudes. This is because a gnomon relies on casting a shadow on the ground. Nearer the equator little or no shadow is cast and further north the light intensity is reduced such that it is difficult to measure. Other devices like a quadrant could also measure inclination.
Angles used in measuring stars, max tilt, obliquity, and equatorial tilt.
20°
1.43° (1.2°)
7.155°
The 0.0392°/day variation along 7.155 equatorial tilt using a distance of 1km to define the horizon angle of 1.0145° with sides of 0.962km/0.042km with a perimeter of 2km. This is a gnomon measurement for east/west and maintains the horizon.
1.0145°/day =365÷1.0145=360
68.67 days or 2.289 months
(=5.32 readings per year)
Here, the errors are defined, and then readings can be taken.
Horizontal
1.0145°/day =365.2425÷360=1.0145°
Vertical
0.0392°/day =14.31÷365.2425=360°
Tilt (rotational)
20÷(25772÷2)=0.00155°
=0.00155×1000=1.55°/1000 years
Obliquity (decreasing)
2.86÷20500=0.0001395°/year
2.40÷20500=0.000117°/year
Obliquity should be considered as subtracting from an increasing tilting in the last 8600 years, and as tilt is decreasing from the 1980s, it should be considered as adding.
Obliquity
Using two numbers, 1.43° an ancient Egyptian derived number and a mean modern day number of 1.2° for obliquity.
Currently considered as a fluctuation from 22.1° to 24.5° about the current tilt of 23.5°, but the exact number is 23.253° as a point. This gives a difference of 1.247° from 24.5° as peak and decreasing and shall continue to do so.
Mid point for 1.43° =23.253° (24.68° peak)
10250÷1.43
7167.832×0.1855=1329
10250-1329=8921-2019=6902 bc
(Difference from 2019, 23.437−23.253=0.1855)
Mid point for 1.2° =23.253° (24.5° peak)
10250÷1.2
8542×0.1855=1584
10250-1584=8665-2019=6646 bc
Obliquity tilt was at its peak 6902 bc or 6646 bc, its precession is for 41000 years, so peak to mid point in 20500 years is 10250 years.
According to recent calculations, the mid point is 23.253° about a 2.4° fluctuation, which hasn't been reached yet.
23.253−23.439=0.1855
0.1855÷0.0001395=1329 years
Peak=(10250−1329)−2019=6902 bc
0.1855÷0.000117=1584 years
Peak=(10250−1584)−2019=6642 bc
A difference of 256 years
So, for the last 20500 years, obliquity was trying to cancel tilt by 1.43°.
15.89°-1.43°.
But from 1980's tilt has been decreasing so for the following 10250 the tilt is
15.89°+1.43°
But obliquity is for 20500 years, so this equates to 9981 years.
Recent calculations suggest the fluctuation is 1.2° about 23.253°
This is 23.4385-23.253=0.1855° away from mid point.
=1584 years from mid point (2011 numbers)
(10250−1584)−2019=6646 bc
So from 2011=6654 bc
As a percentage difference
(12886÷100×67)−1984=6650 bc
After the errors.
Horizontal
1.0145°/day =365.25÷360=1.0145°
1° of variation =51.6-42=9.67m
Vertical
0.0392°/day =14.31÷365.25=360°
1° of variation =25.5 days=18m
=0.7m /day
Tilt (rotational)
20÷(25772÷2)=0.00155°
=0.00155×1000=1.55°/1000 years
1° of variation =645 years
=0.00155°/year=2.7cms/year
Obliquity (decreasing)
2.86÷20500=0.0001395°/year
1° of variation =7167 years
=2.43mm
2.40÷20500=0.000117°/year
1° of variation =8542 years
=2.04mm
These numbers can be adjusted for a 360-day year, and the difference is small, but the use of 1.0145 and not 1.0 suggests that they used a 365.25 day year. Measure for the obliquity probably got averaged out over a 10 year duration, and tilt might have been the same.
Measuring stars
For example, the star Sirius at:
Right ascension
06h 45m 08.91728s
=90.752°
Declination
−16° 42′ 58.0171″
=16.716°
Measures could be used to mark their location for any given year, and as it rotates, the displacement can be measured. The displacement would contain both the error and objects variation, where the error could be subtracted.
Solar Elevation Angle
Temperature Trend Changes
Orbital Climate Change
Archeology77 ©
Comments
Post a Comment